Difference between revisions of "Moving Objects"
| Line 41: | Line 41: | ||
[[Category:View Commands]] | [[Category:View Commands]] | ||
[[Category:References]] | [[Category:References]] | ||
| − | [[Category:Logic]] | + | [[Category:AGI Logic]] |
Latest revision as of 14:01, 30 January 2024
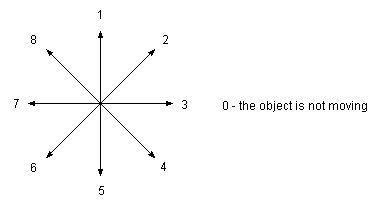
Each object on screen has a direction it is moving in. This is a numerical value from 0 to 8.
When an object is moving normally (and has a direction greater than 0), it will continue moving until it is told to stop, move in another direction, or runs into an obstacle (such as a control line, a block, or another object).
An object’s direction can be changed using the set.dir command. The get.dir command will allow you to find out what it’s current direction is. The direction of ego (object 0) is always stored in v6. To stop an object’s movement, use stop.motion.
There are several commands which will make an object move in different ways:
The normal.motion command will make the object in move in the way described above after it has been moving from one of these three commands.
An object’s step size (the number of pixels moved each step) and step time (the number of interpreter cycles between steps) can be set with the step.size and step.time commands.
Sources
See also
set.dirget.dirstop.motionstart.motionmove.objmove.obj.vwanderfollow.egonormal.motionstep.sizestep.time- Animated Objects